TCFD (Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures)
Joined TCFD Consortium
Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) was established by the Financial Stability Board (FSB) to discuss matters on climate-related disclosures. The Task Force recommends firms and other entities to grasp and disclose the risks and opportunities that climate change poses on their business.
In June 2022, we joined the TCFD Consortium, a group of Japanese companies and financial institutions that support the TCFD recommendations.
TCFD Consortium is an organization established to discuss how companies and financial institutions that support the TCFD recommendations can work together to promote effective corporate disclosure and how disclosed information can be used by financial institutions to make sound investment decisions.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reduction Plan
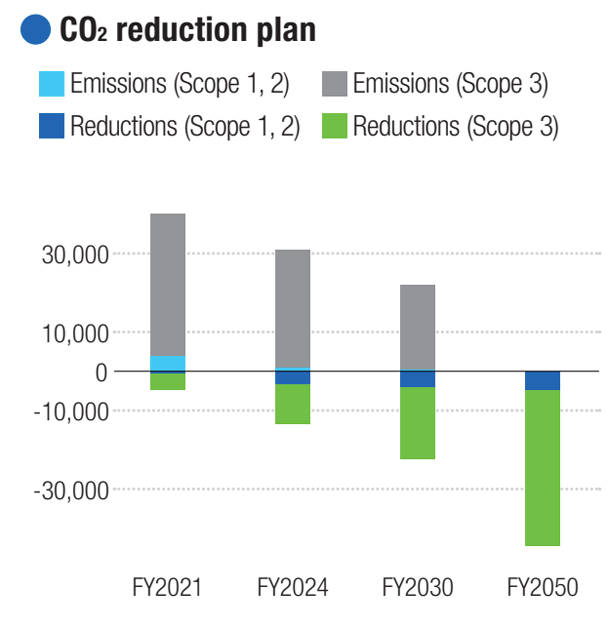
Nippon Signal will work on its own corporate initiative to reduce its greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 50% by 2030 and to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050.
Our plants (manufacturing bases) will be 100% powered by green electricity in 2022. We will concurrently make efforts to reduce emissions from the use of products we have sold.
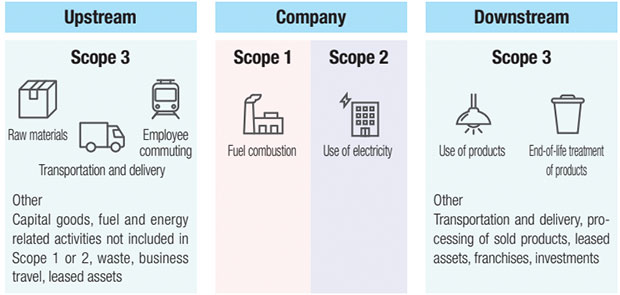
Scope1 : Direct GHG emissions of the company that occur from fuel combustion or industrial processes
Scope2 : Indirect GHG emissions associated with the use of electricity, heat, or steam supplied by electric power companies and other external sources
Scope3 : All indirect GHG emissions resulting from business activities that do not fall into Scope 1 or Scope 2
Initiatives for Environment Beneficial Products, R&D
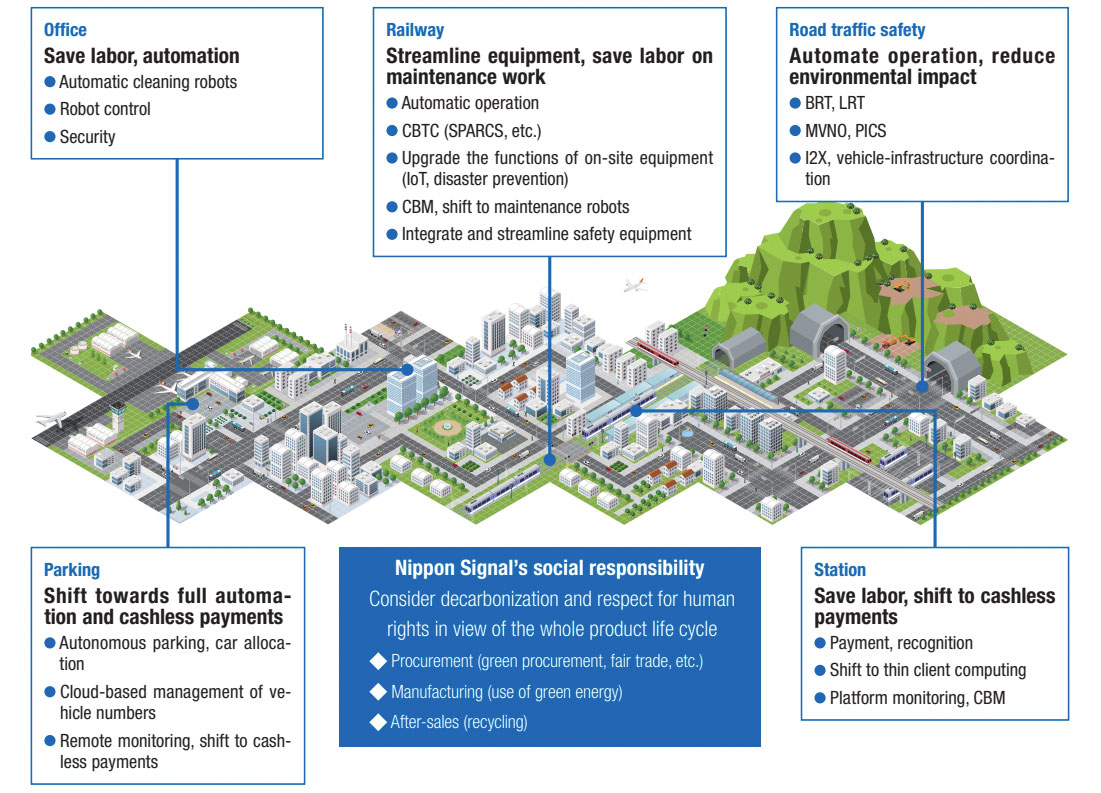
CBTC:Communications-Based Train Control
SPARCS:Simple-structure and high-Performance ATC by Radio Communication System
CBM:Condition Based Maintenance
BRT:Bus Rapid Transit
LRT:Light Rail Transit
MVNO:Mobile Virtual Network Operator
PICS:Pedestrian Information and Communication Systems
I2X:Infrastructure to X
Disclosure in Accordance with TCFD Recommendations
● Governance
Nippon Signal regards the addressing of climate change as a significant sustainability challenge. Our Company-wide Environmental Committee, chaired by the Executive Officer responsible for TQM Promoting Department and involving heads of each site, manages the process in accordance with the targets and plans for each fiscal year. The Board of Directors provides supervision based on the reports on matters and progress.
● Strategy (scenarios adopted)
In considering scenario analyses, we have consulted AR6 SSP1-2.6 and SSP5-8.5 of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and set two scenarios, namely, (1) a world in which the average temperature rise in 2100 is below 2°C (2°C Scenario), and (2) a world in which the average temperature rise in 2100 is 4°C (4°C Scenario)
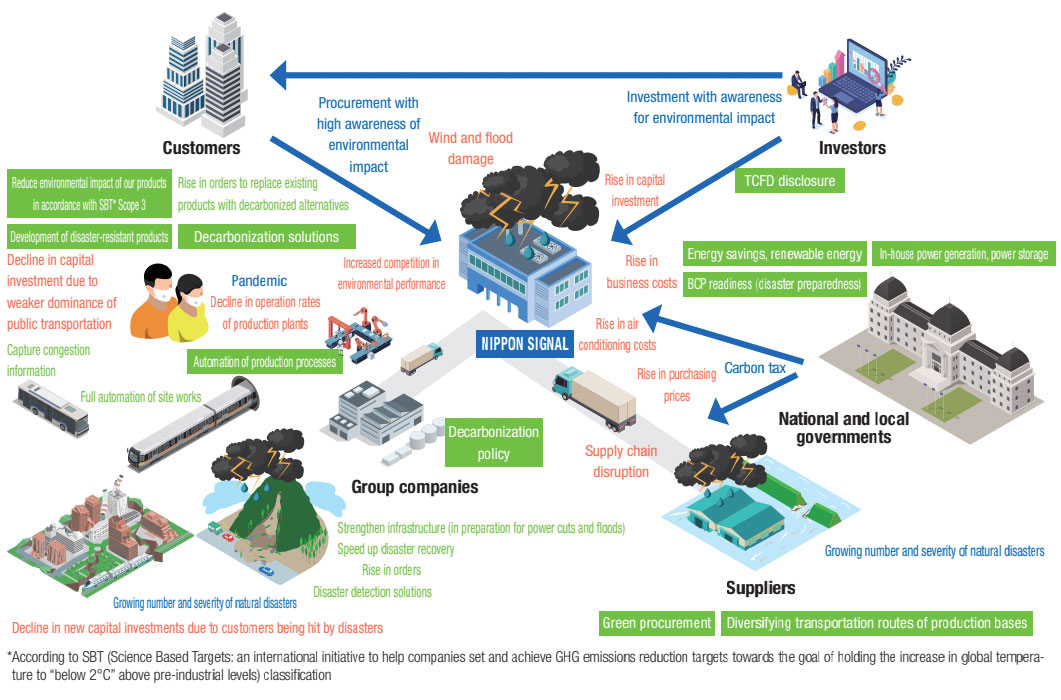
● Risk management
At Nippon Signal, we sort out, evaluate, and manage climate-related risks listed below and deliberate their validity at the Company-wide Environmental Committee.
(1) Transition risks (policy and regulations, market, technology, users’ behavioral changes)
(2) Physical risks (natural disasters, infectious diseases)
● Indicators and targets (life cycle CO2emissions)
Nippon Signal will calculate its GHG emissions according to Scopes 1-3 of STB (Science Based Targets: an international initiative to help companies set and achieve GHG emissions reduction targets towards the goal of holding the increase in global temperature to “below 2°C” above pre-industrial levels) and work to reduce emissions. For Scope 3, we will measure emissions for each category and make efforts to reduce GHG emissions, particularly those related to the use and endof-life treatment of our products, with activities starting in the early design stages.
Strategy Based on Scenario Analyses
According to our analysis, the changes in society to keep the temperature rise below 2°C will bring about carbon taxation and other regulations, changes in market needs, and other changes, and will push up demand for Nippon Signal’s decarbonization solutions. If the temperature increased by 3-4°C, there will be a rise in physical risks associated with severe disasters caused by climate change, and it may seriously affect our supply chain including our own offices and plants. Our analysis also suggests that there will be a rise in demand for disaster-resistant products.
2℃ Scenario
| Risks | Implications for Nippon Signal | Responses of Nippon Signal |
|---|---|---|
| Transition risks | ||
| Carbon tax on suppliers, introduction of emissions trading system |
|
|
| Rapid change in procure- ment and investment behaviors aimed at a decarbonized society |
|
|
*1. Long-term targets for GHG emissions reduction (SBT Scope 3) will be presented in the 6th Stage Environmental Action Plan.
*2. SBT, or Science Based Targets, are the GHG emissions reduction targets required under the Paris Agreement. Scope 3 covers indirect emissions.
4℃ Scenario
| Risks | Implications for Nippon Signal | Responses of Nippon Signal |
|---|---|---|
| Physical risks | ||
| Increased severity and sharp rise in the frequency of natural disasters |
|
|
| Regional epidemic of infectious diseases |
|
|
Opportunities
| Opportunities | Implications for Nippon Signal | Responses of Nippon Signal |
|---|---|---|
| Expand sales of products and solutions that support customers’ decarbonization efforts |
|
|
| Expand sales of products and solutions that support the strengthening of customers’ infrastructure |
|
|
| Expand sales of solutions that will help counter infectious diseases (new normal) |
|
|
| Create and expand new businesses |
|
|
Trends in Life Cycle CO2 Emissions
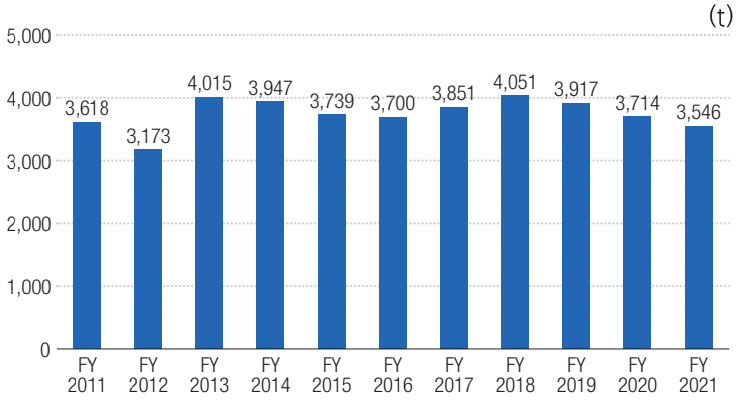
● Trends in Scope 1, 2 emissions
● Emissions from main Scope 3 categories and calculation method
We estimate CO2 emissions from categories that are thought to account for a large portion of total emissions from our corporate activity. We plan to cover more categories and also review the calculation method to improve the accuracy of figures.